Ergonomic challenges in Healthcare-related transport
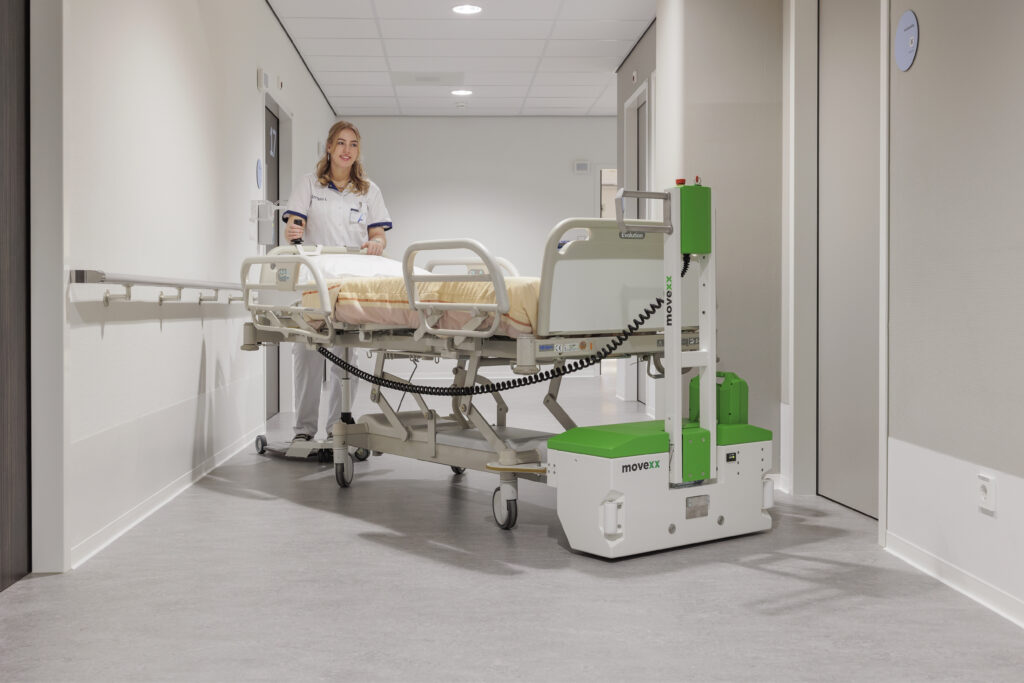
In healthcare environments, it is common for materials or patients to be moved manually for example, pushing wheelchairs, beds, or trolleys, or repositioning patients using a slide sheet. While these practices help reduce heavy lifting, they still require physical effort, often in awkward postures. This can lead to physical strain and other ergonomic risks.

Main Physical Complaints
Lower back pain: A significant proportion of healthcare workers worldwide report experiencing lower back pain each year as a result of bending, exerting force, and pushing or pulling heavy loads. This type of pain affects not only employee comfort but also their work capacity.
Neck and shoulder pain: Common complaints among healthcare workers include pain caused by pushing and maneuvering beds and carts, which can lead to overload of the neck muscles and shoulder girdle. These issues can range from muscle tension to inflammation and wear-and-tear injuries.
Other complaints: Arm and wrist pain, as well as upper back pain, are also reported, although less frequently.
Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders in Healthcare
International data show that the vast majority of healthcare workers experience musculoskeletal disorders each year, with rates varying depending on the region and type of complaint.
Impact on Absenteeism and Long-Term Work Disability
These ergonomic issues result in substantial costs and staffing challenges for healthcare institutions. Musculoskeletal disorders are a major cause of sick leave and can lead to long-term work disability.
Conclusion
Reducing ergonomic risks requires effective measures, such as using appropriate assistive equipment and providing ergonomic training. These approaches not only contribute to the health and employability of healthcare workers, but also to the overall efficiency of healthcare facilities and hospitals.
For more information visit: movexx.com
News Categories
- » NEWS HOME
- » Automation & Robotics
- » Industry 4.0
- » Material Handling
- » Sensors
- » Quality & Testing
- » Machine Vision
- » Laser & Optics
- » Metalworking
- » Motion Control & Drives
- » Hydraulics & Pneumatics
- » Process Industry
- » Renewable Energy
- » Agriculture
- » Home & Office Furniture
- » Additive Manufacturing
- » Environmental Tech



